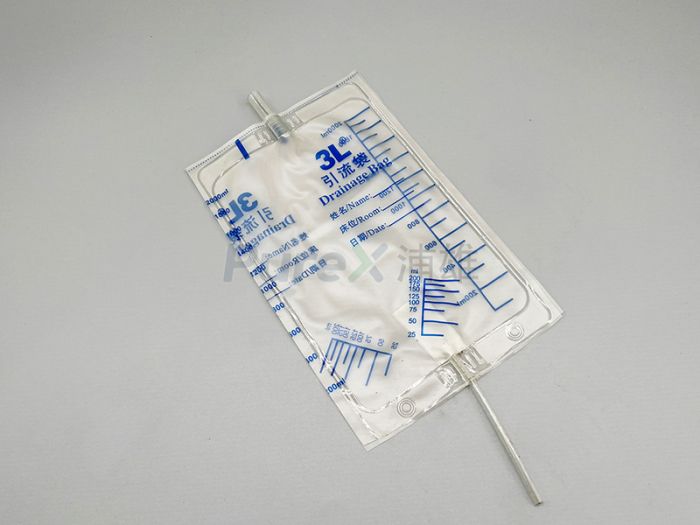
Analysis of the Material of the drainage Bag and Detailed Explanation of Key Technologies in the heat Sealing process
I. Introduction to Drainage Bag Materials
As critical devices for fluid collection in medical settings, drainage bags must balance biosafety, flexibility, and durability. Below is an analysis of the key characteristics of mainstream materials:
1. TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
Core Advantages:
- Excellent biocompatibility, compliant with ISO 10993 medical-grade standards; no cytotoxicity or sensitization risks.
- Tear resistance of 50–80 MPa (ASTM D638 standard); puncture resistance 3× higher than PVC, withstanding impacts from sharp fluids (e.g., stone fragments).
- Strong chemical resistance, tolerates complex fluids (e.g., urine, bile) without swelling during long-term use.
Applications: High-end drainage systems, long-term indwelling devices.
2. Medical-grade PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Core Advantages:
- 40%–60% lower cost than TPU, suitable for large-scale disposable use.
- High transparency (light transmittance ≥90%), facilitating fluid observation.
Limitations: - Plasticizers (e.g., DEHP) pose migration risks; restricted under EU REACH regulations.
- Brittle at low temperatures; storage temperature must be ≥-10°C.
3. EVA (Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer)
Core Advantages:
- Superior flexibility (Shore A hardness 60–80), conforming to body contours and reducing pressure on patients.
- Odor level ≤2 (per VDA 270 standard), enhancing patient comfort.
Applications: Postoperative short-term drainage, home care scenarios.
II. Key Technologies in Drainage Bag Heat Sealing Processes
Heat sealing directly impacts sealing integrity and safety. Below is a comparison of mainstream techniques:
1. High-Frequency (HF) Welding
Principle:
High-frequency electric fields (13.56–40.68 MHz) induce dipole vibration in TPU molecular chains, generating frictional heat for fusion.
Advantages:
- Weld strength ≥85% of base material (ASTM F88 standard); burst pressure ≥300 kPa.
- Heat-affected zone <0.5 mm, preventing material degradation.
Quality Control: - Real-time monitoring of welding energy (1–5 kJ), pressure (0.2–0.5 MPa), and time (0.5–3 s) to ensure weld consistency.
2. Ultrasonic Welding
Principle:
20 kHz ultrasonic vibrations generate interfacial friction heat, combined with 0.1–0.3 MPa pressure for bonding.
Advantages:
- Cycle time <1 s, 3× faster than HF welding.
- Suitable for micro-connectors (e.g., drainage tubes ≤5 mm diameter).
Limitations: - Weld strength 20%–30% lower than HF welding; requires reinforcement design.
3. Hot Plate Welding
Principle:
Heating material surfaces to 180–220°C via hot plates, followed by pressurization after plate removal.
Advantages:
- Ideal for heat-sensitive materials like PVC, minimizing plasticizer volatilization.
- Weld smoothness ≤0.1 mm, reducing fluid residue risks.
Quality Control: - Strict control of temperature fluctuation (±2°C) and contact time (5–10 s) to prevent carbonization.
III. Process Optimization Directions
-
Multilayer Composite Sealing
TPU/EVA/TPU tri-layer structures improve strength and flexibility, boosting burst pressure by 40%. -
Online Inspection Systems
Infrared thermography for real-time weld temperature monitoring; automatic alarms for deviations >5°C. -
Eco-Friendly Sealing
Development of water-based barrier coatings to replace plasticizers, aligning PVC with RoHS 2.0 standards.
Conclusion
Material selection and heat sealing processes for drainage bags must balance safety, functionality, and cost. High-frequency welded TPU is becoming mainstream due to superior performance, while ultrasonic welding shows promise in miniaturization. Future advancements in smart sealing equipment and bio-based materials will drive safer, greener evolution in drainage bag technology.