Blood pressure cuff liner and its production technology
I. Overview of Blood Pressure Cuff Bladder
The blood pressure cuff bladder is typically made of soft yet durable materials such as rubber or plastics (e.g., TPU, PVC). These materials are selected to balance robustness and flexibility, ensuring a snug fit around the patient’s upper arm during blood pressure measurement while preventing discomfort or skin damage.
The design of the cuff bladder also adheres to mechanical requirements, enabling secure fastening to prevent slippage. During measurement, the bladder inflates to compress the artery and obtain blood pressure readings. If the bladder lacks durability or is overly loose, the cuff may fail to fit properly, compromising measurement accuracy. Conversely, excessive rigidity or tightness in the bladder may restrict blood flow, similarly affecting accuracy.
II. Production Process
The production process for blood pressure cuff bladders is relatively complex but can be broadly divided into the following steps:
-
Material Preparation: High-quality raw materials, such as TPU or PVC films, are prepared. These materials must meet environmental, non-toxic, and odorless standards to ensure product safety.
-
Cutting: Cutting equipment is used to slice roll materials into individual sheets of appropriate size. Precision and efficiency in this step are critical for subsequent heat sealing.
-
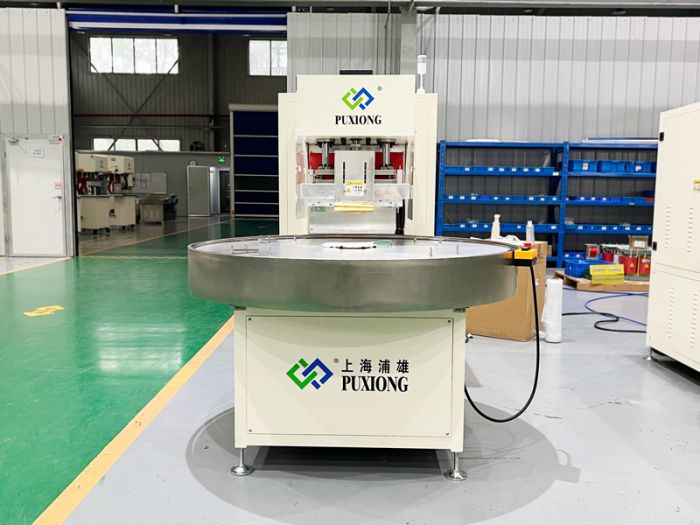
Heat Sealing and Welding: The cut sheets undergo heat sealing. This step typically employs high-frequency machines (high-cycle machines) or conventional heat-sealing equipment.
- High-frequency machines generate high-frequency electromagnetic waves, inducing internal vibration and friction within the material to convert into heat for sealing.
- Conventional heat-sealing devices use heating elements to melt and bond material surfaces.
- Parameters such as temperature, pressure, and duration must be tightly controlled to ensure sealing quality and consistency.
-
Trimming and Collection: After sealing, the products are trimmed into individual cuff bladders and collected into bins for inspection and packaging.
For large-scale production, automated production lines may be utilized to minimize manual intervention, reduce labor intensity, and enhance stability and uniformity. These lines typically include stations for roll feeding, automatic detection, material dragging, screening, heat sealing, material pulling, and cutting. Automation significantly boosts productivity and operational efficiency.