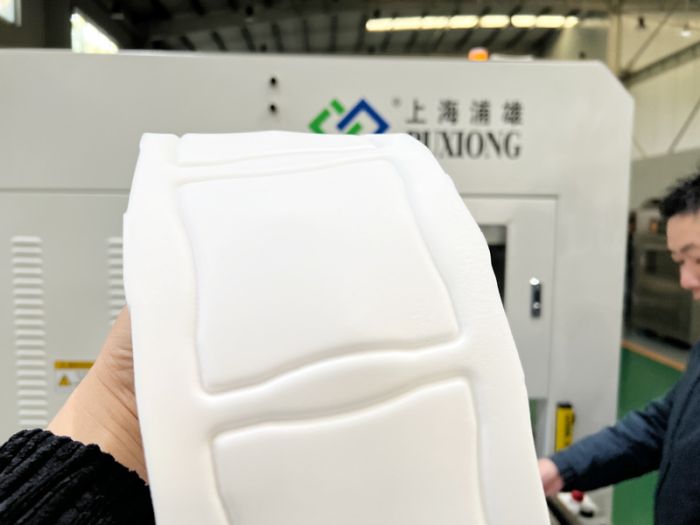
Key factors to consider when designing the lead screw shield for aseptic production workshops
I. Material Selection
-
Aseptic Compatibility:
- Select materials harmless to sterile environments, avoiding substance release that contaminates production areas.
- Materials should be easy to clean and disinfect to maintain sterility long-term.
-
Corrosion Resistance:
- Materials must exhibit strong corrosion resistance to withstand potential corrosive agents during production.
-
Wear Resistance and Strength:
- Materials should possess sufficient wear resistance and mechanical strength to endure friction and impact forces during lead screw movement.
II. Sealing Performance
-
Dustproof and Waterproof:
- The protective cover must provide effective dustproof and waterproof capabilities to prevent contaminants and moisture from entering the lead screw system.
-
Microbial Intrusion Prevention:
- Design must address microbial entry pathways, ensuring tight seals at edges, joints, and interfaces to block bacteria, mold, and other microorganisms.
III. Structural Design
-
Flexibility:
- The protective cover should move freely with lead screw extension/retraction without hindering normal operation.
-
Detachability:
- Design should allow easy disassembly and reinstallation for cleaning, disinfection, and maintenance.
-
Visibility and Maintenance Accessibility:
- The cover should permit visual inspection of the lead screw and facilitate maintenance tasks when needed.
IV. Dimensions and Geometry
-
Precision Fit:
- Dimensions and shape must precisely match lead screw specifications to ensure optimal protection.
-
Environmental Adaptability:
- Account for sterile workshop conditions (temperature, humidity, pressure) to maintain functionality under operational constraints.
V. Cleaning and Disinfection
-
Ease of Cleaning:
- Smooth, crevice-free surfaces (internal/external) enable efficient use of cleaning agents and disinfectants.
-
High-Temperature Disinfection Tolerance:
- Materials must withstand sterilization methods such as steam or dry heat treatments.
VI. Safety
-
Operational Safety:
- Design should prevent accidental contact with moving lead screw components to avoid injuries.
-
Flame Retardancy:
- Materials should exhibit fire-resistant properties to prevent flame propagation in case of fire.
VII. Economic Considerations
-
Cost-Effectiveness:
- Prioritize cost-efficient materials and designs while meeting all technical requirements.
-
Service Life:
- Ensure long-term durability to maintain sterility and protective performance throughout the product lifecycle.