Infusion pressure bag and heat sealing process
I. Overview of Infusion Pressure Bags
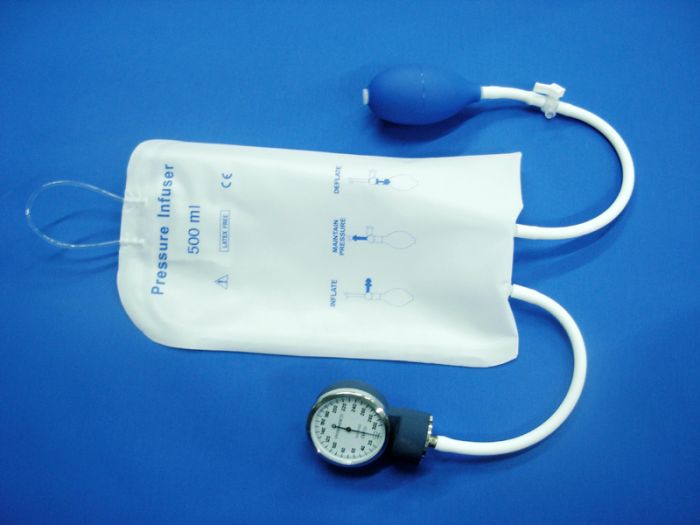
The infusion pressure bag, also known as an infusion pressure bag, is primarily used for rapid pressurized infusion during blood transfusion or fluid administration to facilitate the quick delivery of blood, plasma, cardioplegia solutions, or other bagged liquids into the human body. It can also continuously pressurize heparin-containing fluids to flush indwelling arterial pressure monitoring catheters. This product is user-friendly, safe, and reliable, making it essential for emergency medical care in battlefields, remote settings, and clinical environments.
The infusion pressure bag consists of a storage airbag, hanging straps, a fluid bag fixation membrane, tubing, air valves, and an inflation bulb. Key technical specifications include:
- Air-tightness: The bag must maintain integrity with no leakage for at least 3 hours.
- Load-bearing capacity: The hanging straps must support a weight of 1 kg.
II. Heat Sealing Process for Infusion Pressure Bags
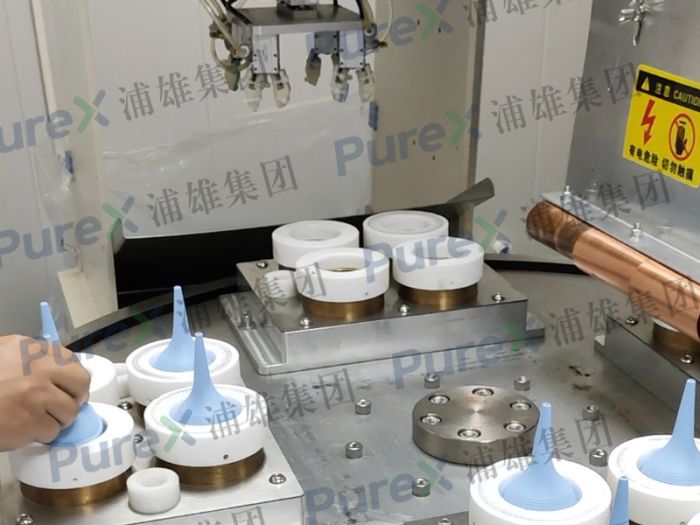
The heat sealing process is a critical step in the production of infusion pressure bags, directly impacting their sealing performance and overall quality. Below is a detailed analysis of the heat sealing process:
1. Material Preparation
- Select materials meeting medical-grade standards, such as PVC or TPU, which offer excellent pressure resistance, corrosion resistance, and sealing properties.
- Pretreat materials (e.g., cleaning and decontamination) to ensure optimal heat sealing results.
2. Equipment Calibration
- Calibrate the heat sealing equipment to ensure optimal performance.
- Set precise parameters for temperature, pressure, and duration. These parameters are crucial:
- Temperature: Excessively low temperatures may result in poor sealing, while excessively high temperatures risk damaging the membrane.
- Duration: Insufficient time leads to incomplete fusion, while excessive time may deform or scorch the material.
- Pressure: Appropriate pressure ensures tight bonding by promoting material diffusion during melting. Excessive pressure, however, may displace sealing materials, causing partial cuts or membrane damage.
- Verify the functionality of heating elements, pressure systems, and other critical components.
3. Heat Sealing Operation
- Place pretreated materials into the heat sealing equipment and execute the process using preset parameters.
- Continuously monitor material melting, bond quality, and seal integrity during operation. Adjust parameters in real time to ensure consistency.
4. Quality Inspection
- Perform post-sealing quality tests, including sealing integrity and strength assessments, to verify compliance with standards.
5. Optimization Strategies
- Use high-precision, stable heat sealing equipment to ensure process consistency.
- Optimize mold materials (e.g., mold steel, beryllium copper, or aluminum alloys) with high thermal conductivity and minimal deformation.
- Develop detailed operating procedures and provide staff training to standardize operations.
- Implement automated control systems and sensors for real-time monitoring. Establish data analysis and feedback mechanisms to address issues promptly.
- Continuously refine parameters and processes based on production data and feedback.
III. Application of High-Efficiency Heat Sealing Technology
Advanced heat sealing technology enhances both the sealing performance of infusion pressure bags and production efficiency. By optimizing parameters and workflows, rapid and precise sealing reduces production cycles. Rigorous quality control ensures consistent sealing integrity and product reliability, elevating overall quality.