Detailed explanation of anti-toxic suits and electric heating welding machines
I. Overview of Chemical Protective Clothing
Chemical protective clothing, as the name suggests, is designed to shield wearers from toxic substances such as harmful gases, vapors, and smoke. With the growth of industries like chemicals, petroleum, and pharmaceuticals, demand for such protective gear has surged. Its primary function is to block toxic substances from entering the respiratory tract or contacting the skin. Current market offerings include half-mask, full-face mask, and full-body suits, tailored to diverse work environments and operational requirements.
.jpg)
II. Key Technical Specifications
-
Sealing Performance
The clothing must ensure airtightness to prevent toxic leakage via masks or tubing. Compliance with the GB 2828 standard is typically required for sealing quality grading. -
Protective Performance
Effective resistance to toxic gases, vapors, and smoke is critical, measured by metrics like Protection Factor (PF) and Filtration Speed (FM) to safeguard respiratory systems, eyes, and skin. -
Comfort
Lightweight design, proper sizing, and low breathing resistance are essential to minimize wearer fatigue. -
Durability
Longevity and stable protective performance under harsh conditions are mandatory. -
Ease of Use
Easy donning/doffing, cleaning, and anti-static properties (to prevent spark-induced hazards) are prioritized.
III. Manufacturing Equipment for Protective Clothing
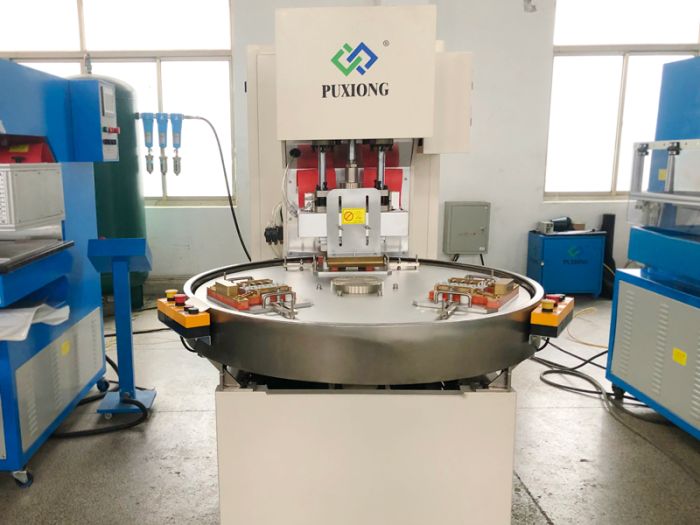
Specialized equipment, including electric heating welding machines, is vital for meeting technical standards. These machines are critical for producing sealed seams, gaskets, and other components.

-
Working Principle of Electric Heating Welding Machines
Heat generated by electrical resistance melts workpiece surfaces, followed by pressure application to form bonds. Advantages include simple operation, rapid welding, and minimal heat-affected zones. -
Key Components
- Power Supply: AC/DC power sources.
- Control System: Adjusts parameters (current, voltage, time).
- Heating Elements: Nichrome wires or heating plates.
- Worktable: Adjustable platform for positioning workpieces.
- Welding Torch: Directs the arc and controls welding speed.
- Cooling System: Prevents post-weld deformation or cracking.
IV. Applications in Protective Clothing Production
-
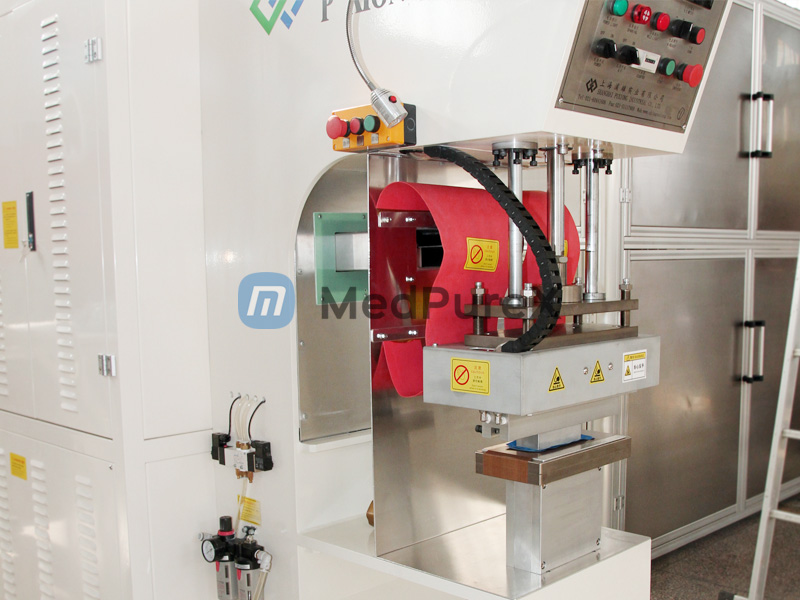
Gasket Fabrication
Electric heating welders ensure precise temperature/time control for bonding respirators to suits, preventing toxic leakage. Thermoforming processes are often used for specialized gasket materials. -
Seam Welding
High-strength seams in critical areas (collars, cuffs) are efficiently welded, reducing reliance on labor-intensive stitching and enhancing structural integrity. -
Other Component Assembly
- Zippers/Buttons: Resistance welding secures metal parts.
- Ultrasonic Welding: High-frequency vibrations fuse materials (e.g., synthetic fabrics).